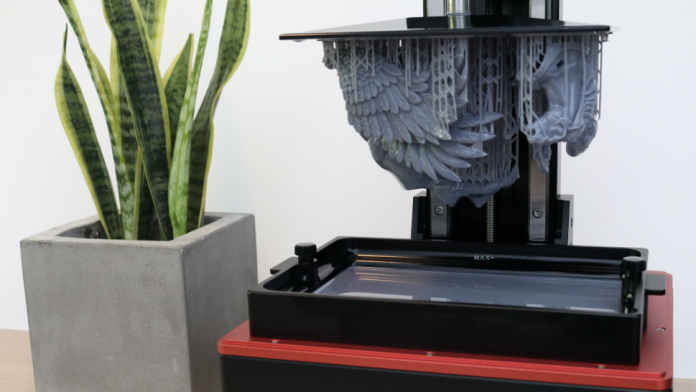
Without a doubt, 3D printing technology has made a major breakthrough in recent years, particularly with the advent of resin printers. These cutting-edge devices offer a multitude of applications across different industries, which made a significant impact on the way we design, manufacture and innovate.
Their versatile and innovative features have transformed traditional manufacturing processes allowing entrepreneurs who are running a small business to create customised prototypes and and intricate designs with ease and precision. If you’re eager to learn more about the unique characteristics of these unique devices and delve deeper into their application and uses, you’ve come to the right place.
Prototyping and Product Development
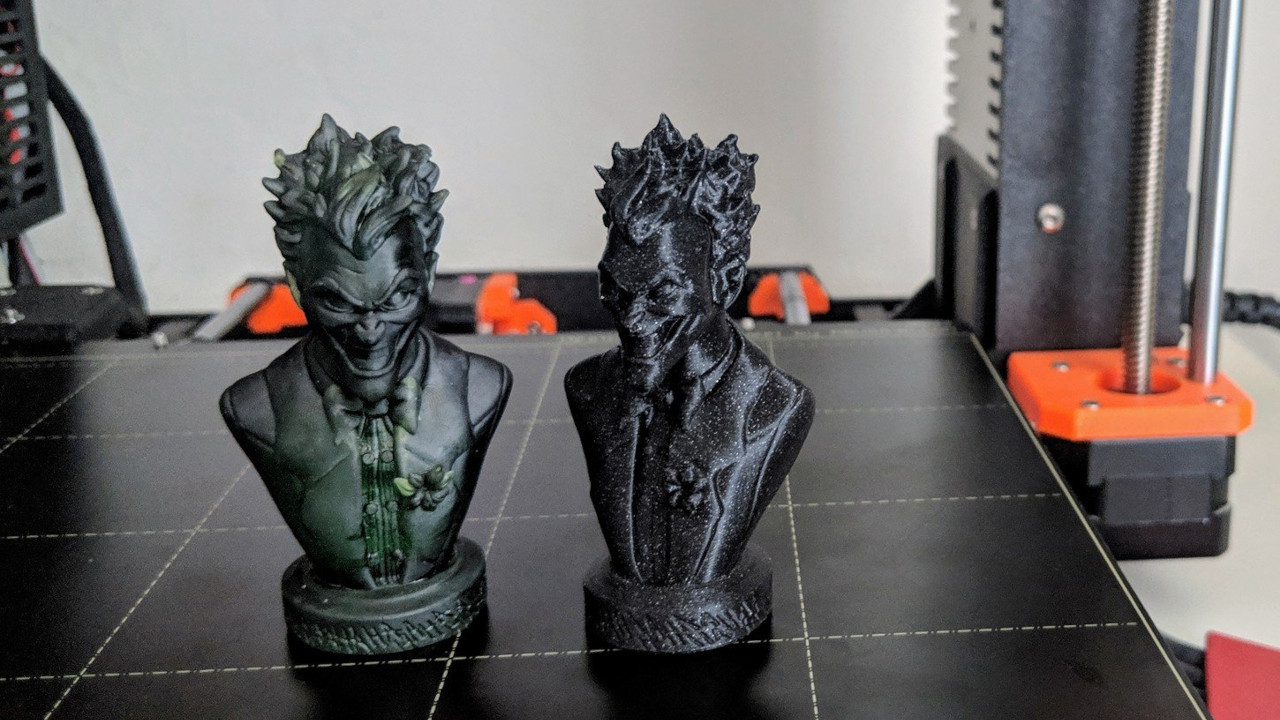

The 3D printers, in particular resin-based, have revolutionised the field of prototyping and product development. While, in the past, this was considered a time-consuming and costly process, nowadays designers and engineers can rapidly iterate on their designs and concepts to produce prototypes with intricate features and exceptional accuracy and complexity. Advanced printers with pigmented and easy-to-use 3D resin filaments solidify the material into precise shapes and forms which may be difficult to achieve with traditional printing methods.
By using these unique devices, intricate geometric and fine details are produced which enables the creation of highly detailed and visually stunning prototypes that accurately represent the intended design. This feature allows for the product to undergo thorough testing, evaluation, and refinement before it moves into full-scale production.
In addition to these advantages, the resin-based 3rd printers are particularly useful for creating personalised prototypes that cater to individual needs and specific requirements. This is especially beneficial across industries such as healthcare where customised medical devices and implants can be made to meet the unique anatomical characteristics and medical needs of individual patients.
Jewellery Making
In addition to being especially beneficial for producing exceptional prototypes with high precision, these printers have been incredibly useful in other fields, such as jewellery making. What makes the 3d resin-based printer particularly advantageous for this craft is its ability to produce highly detailed and intricate designs with smooth surfaces and flawless finishes.
This allows jewellery makers to create customised pieces with ease and explore various innovative techniques when creating their designs. For instance, they may experiment with different materials and finishes or explore advanced technologies like 3D scanning and computer-aided design (CAD) to create visually striking and captivating jewellery pieces.
To further embellish their design, jewellery makers may also incorporate traditional craftsmanship techniques such as stone setting, or engraving to add depth and enhance the aesthetic appeal of their final pieces. This fusion of old and new methods allows artisans to unleash their creativity and push beyond the boundaries of traditional jewellery-making when crafting their distinctive pieces of art.
Medical Application
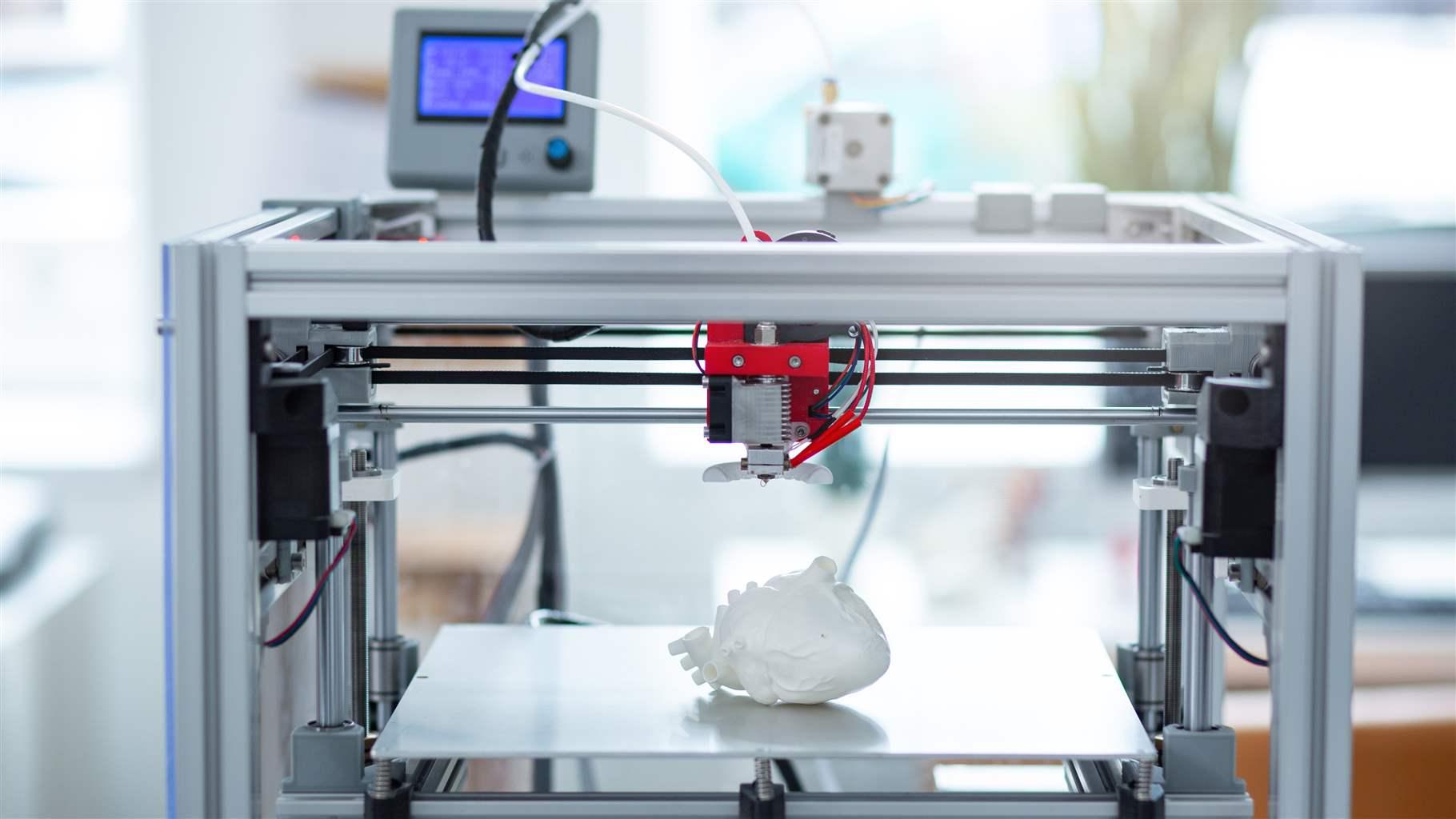

Beyond the realm of jewellery making, resin-based 3d printers have made a significant impact in the medical field, revolutionising the way anatomical models, surgical guides and prosthetics are made. For example, these advanced devices enable surgeons to create unique anatomical models that cater to the patient’s specific anatomy and needs.
This is especially beneficial for pre-operative procedures as surgeons can plan, visualise and anticipate potential challenges that may arise during surgery. These models are accurately designed to closely resemble the patient’s unique anatomy. For instance, before performing complex brain surgery, the surgeon can use these printers to create a 3d printed model of the patient’s skull and brain to simulate the actual procedure and identify potential challenges and outcomes.
This enables surgeons to create a detailed surgical plan and reduce the risks of complications during the actual procedure. The advanced approach to prosthetic design represents only a tiny fraction of the myriad of medical purposes for which these printers are used which only shows how powerful and truly versatile the 3d resin-based technology truly is.
Education and Research
In addition to all of these unique applications, resin-based printers serve as valuable tools for various other educational and research purposes. For example, these advanced instruments are widely used in elementary schools and universities to teach students complex concepts and ideas related to subjects like, math, science, technology and engineering.
These enable students to become more creative and get a better understanding of difficult and abstract concepts. For example, this method can be applied in physics and math to create three-dimensional representations of celestial bodies, astronomical phenomena, and geometric shapes.
These visual models allow students to get a deeper understanding of complex and abstract concepts such as gravitational forces, planetary motion and mathematical equations and encourage the development of their problem-solving and critical-thinking skills. They are further used in many other fields like archaeology, engineering, geology and computer science, contributing to the development of unique techniques and innovation in each one of these educational disciplines.
Even in research settings, resin-based printers play a crucial role. They enable scientists and researchers to create highly detailed and accurate prototypes of their ideas, allowing them to test and improve designs before moving on to the expensive process of mass production. These printers are also used in creating custom-made equipment for specific experiments, saving time and resources that would otherwise be spent ordering from external providers or building them from scratch.